HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM (যকৃত ও পিত্ত সংবহণতন্ত্র্র)
(Help to Metabolism of Food)
System Description :
Having to do with the liver plus the gallbladder, bile ducts, or bile. For example, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) can be applied to the hepatobiliary system. Hepatobiliary makes sense since "hepato-" refers to the liver and "-biliary" refers to the gallbladder, bile ducts, or bile.
Functions of the biliary system :
> The biliary system's main function includes the following :
> Bile is the greenish-yellow fluid (consisting of waste products, cholesterol, and bile salts) that is secreted by the liver cells to perform 2 primary functions :
Bile salt is the actual component that helps break down and absorb fats. Bile, which is excreted from the body in the form of feces, is what gives feces its dark brown color.
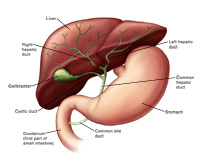
Parts of the Hepatobiliary System :
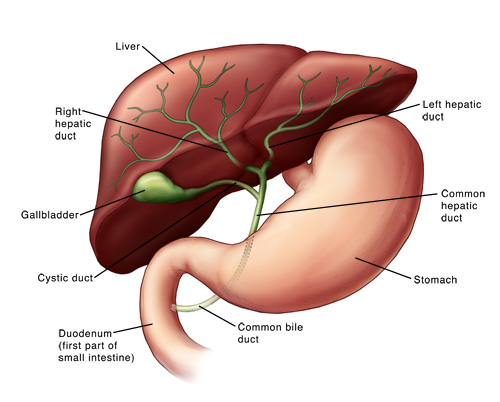
The biliary tract, (biliary tree or biliary system) refers to the liver, gall bladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and conjugated bilirubin.
What are the different types of liver disease? The different types of liver disease are Cirrhosis, Alcohol abuse, Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, Epstein Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis), Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Iron overload (hemochromatosis).
C3.1) Liver disease : Liver disease refers to any disorder of the liver. ... Cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver. Inflammation (hepatitis) from infectious (hepatitis B, hepatitis C) or non-infectious causes (chemical or autoimmune hepatitis) Tumors, benign and malignant (liver cancer) Metabolic disorders.
C3.2) Liver Cirrhosis : Cirrhosis is a late stage of scarring (fibrosis) of the liver caused by many forms of liver diseases and conditions, such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. The liver carries out several necessary functions, including detoxifying harmful substances in your body, cleaning your blood and making vital nutrients.

Thank you for your interest !
This page is comming soon


